Tuberculosis Blood Test
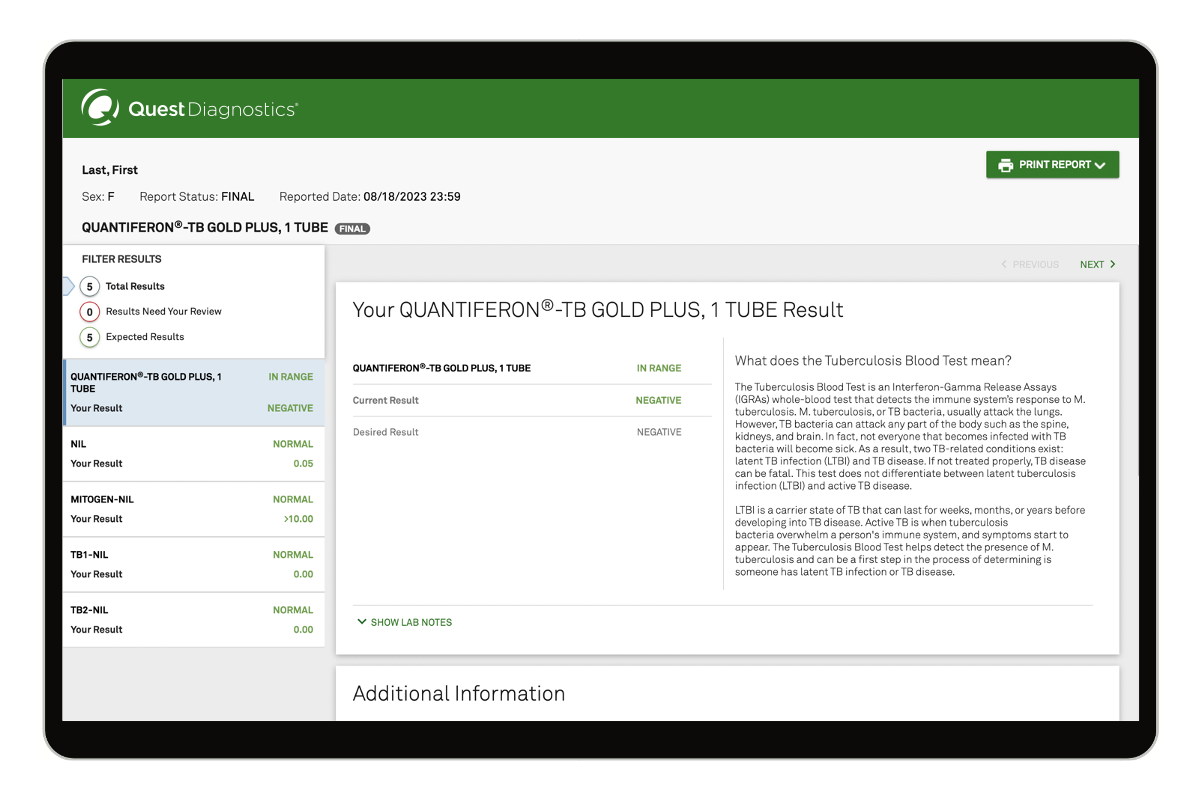
The TB test detects immune response to tuberculosis bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) in your body. It’s intended for those who have been exposed to TB, have a high risk for contracting TB, or require evidence of a negative TB test result. Read moreThis is an Interferon-Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) TB blood test that detects the immune system’s response to tuberculosis bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis attack the lungs but can also attack any part of the body (e.g., spine, kidneys, brain). Not all TB bacteria infections result in sickness. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection (LTBI) and TB disease. If not treated properly, TB disease can be fatal.
LTBI is a carrier state of TB that can last for weeks, months, or years before developing into TB disease. Active TB is when tuberculosis bacteria overwhelm a person's immune system, and symptoms start to appear. While it does not differentiate between LTBI and active TB disease, this tuberculosis blood test detects the immune response to TB bacteria which can be the first step in diagnosing either condition. Further testing may be required if the blood test is positive.
With Quest®️, you can buy a TB blood test online and get testing at a nearby location – no doctor’s visit required.
How it works
questhealth.com offers 100+ consumer-initiated Quest Diagnostics lab tests to empower you to have more control over your health journey. Choose from a variety of test types that best suit your needs.
- The results are either positive or negative, and have a lower risk of reader bias when compared to a skin test
- Accuracy is not affected by a prior bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) TB vaccination
- Only requires a single patient visit (2 to 4 are required for the TST)
Live-virus vaccines may affect IGRA test results. However, the effect of live-virus vaccination on IGRAs has not been studied. Until more information is available, the CDC recommends that IGRA testing for live-virus vaccinations are performed as follows:
- Either on the same day as a live-virus vaccination or 4 to 6 weeks after the administration of a live-virus vaccination
- At least 1 month after a smallpox vaccination
You should not delay a COVID-19 vaccination due to testing for TB. The COVID-19 vaccine is not a live-virus vaccine. It does not affect the results of the TB blood test.
*Data and Statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/statistics/default.htm
**Tuberculosis (TB) https://www.cdc.gov/tb/