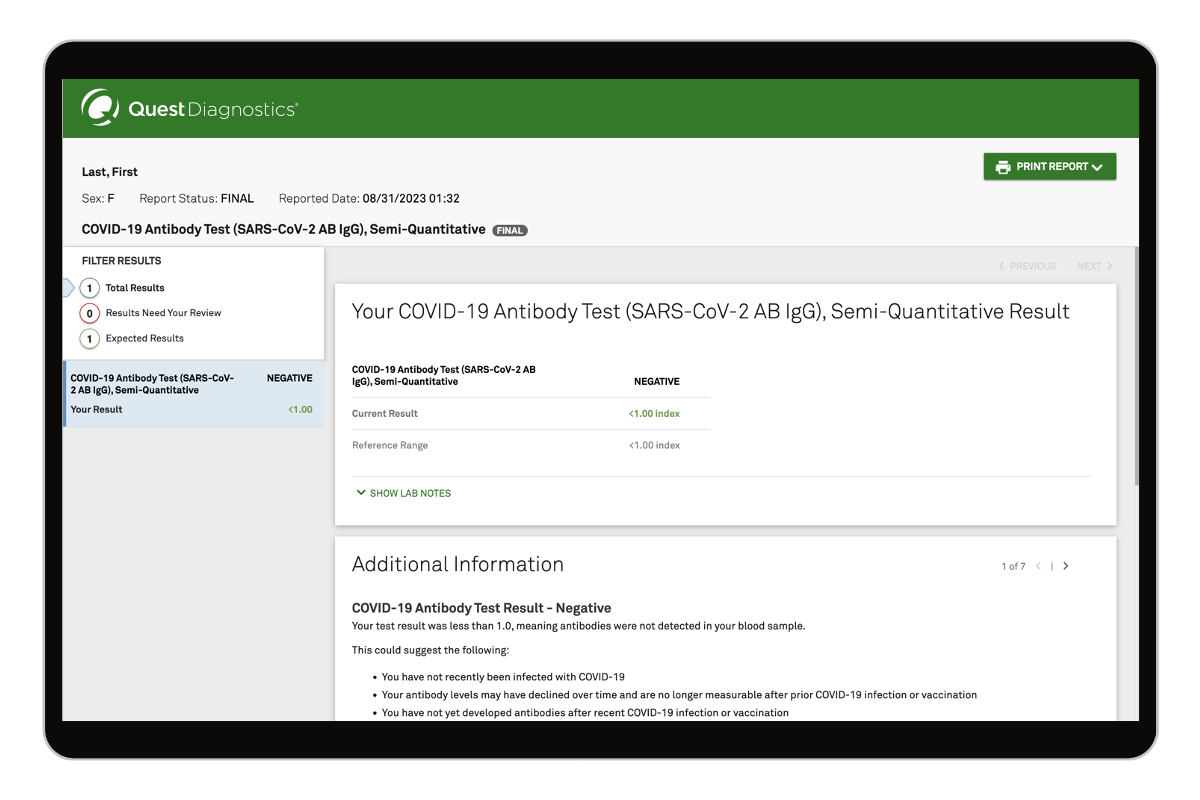
How it works
questhealth.com offers 100+ consumer-initiated Quest Diagnostics lab tests to empower you to have more control over your health journey. Choose from a variety of test types that best suit your needs.
- In-person
- In-home sample collection
Buy a lab test
No doctor visit is required for purchase.
2Register your test
& schedule an appointment
Book a visit to one of 2000+ Quest locations.
3Visit Quest for sample collection
Complete your test sample collection during your scheduled appointment.
4Get fast results
Access results online as soon as they’re available. You will be emailed when they are ready. Discuss your results with an independent physician at no extra cost. Treatment options may be available.
Buy a lab test
+ in-home sample collection
No doctor visit required for purchase. If in-home service is available in your area, purchase for an additional $79 fee.
2Register your test
& schedule an appointment
After you make a purchase, register your test and Quest Mobile will contact you to schedule an in-home sample collection appointment.
3In-home sample collection
A Quest Mobile phlebotomist will collect your sample and deliver it to Quest Diagnostics.
4Get fast results
Access results online as soon as they’re available. You will be emailed when they are ready. Discuss your results with an independent physician at no extra cost. Treatment options may be available.